Cyber Technology & Training Center
Menu
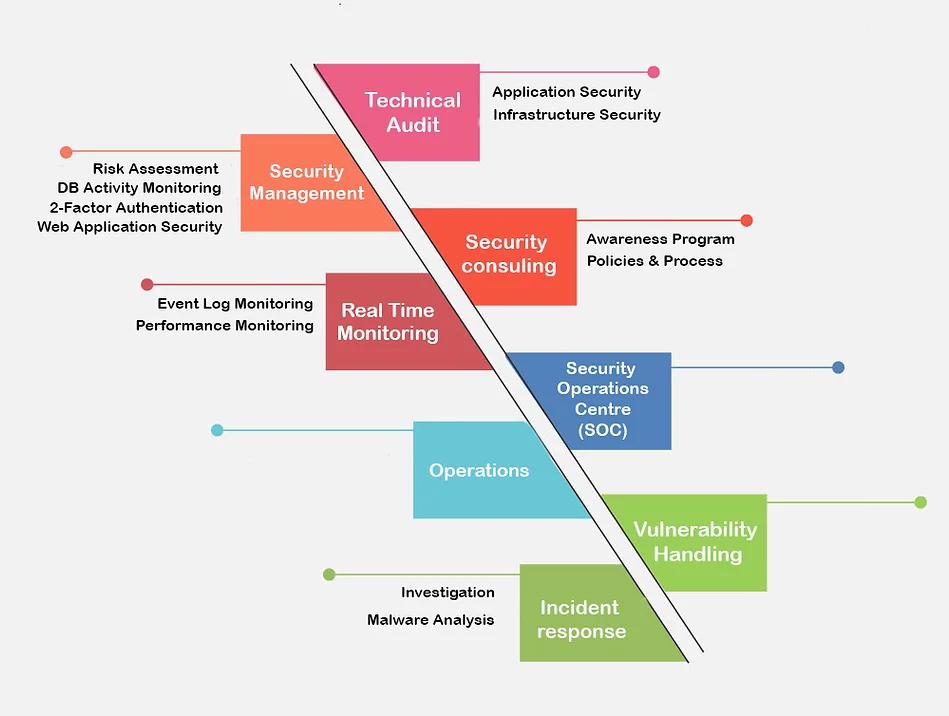
Security Audit
A security audit is an evaluation of a company’s information systems and infrastructure to identify vulnerabilities and potential threats to the organization’s security. Some features of a security audit include
- Risk assessment: The security audit starts with identifying and evaluating potential risks and threats to the organization's assets, including its data, networks, and systems.
- Vulnerability assessment: The auditor identifies vulnerabilities in the organization's security infrastructure, such as outdated software, misconfigured systems, or unsecured access points.
- Penetration testing: The auditor simulates attacks on the organization's systems and networks to identify weaknesses in the security system.
- Compliance review: The auditor reviews the organization's compliance with regulatory standards and industry best practices, such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS, ISO, etc.
- Physical security review: The auditor examines the organization's physical security measures to ensure that they are adequate to protect against theft, damage, or other threats.
- Security policy review: The auditor examines the organization's security policies and procedures to ensure that they are up-to-date, comprehensive, and effective.
- Incident response planning: The auditor examines the organization's incident response plan to ensure that it is effective in mitigating security breaches and restoring normal operations.
- Training and awareness: The auditor evaluates the organization's training and awareness programs to ensure that employees are aware of security risks and have the knowledge and skills to avoid them.
- Risk management: The auditor evaluates the organization's risk management strategy to ensure that it is comprehensive and effective in mitigating risks.
- Report and recommendations: The auditor provides a comprehensive report of findings, risks, and recommendations for improvement.